What’s Slowing Things Down? Discover the Invisible Force at Play
Friction Lesson Plan For Class 8
Hook
Imagine you’re sliding down a super smooth slide but halfway through, you suddenly stop! No one pushed you. No one stopped you. What happened?
Learning Objectives
By the end of this post, you’ll be able to:
- Understand what friction is and how it acts on moving objects.
- Explore the causes and different types of friction.
- Identify factors that affect friction.
- Recognize how friction helps us and when it causes problems.
- Discover ways to reduce or increase friction based on need.
- Learn about fluid friction and why streamlined shapes matter.
Curiosity Questions
- Why do car tires have grooves?
- How do penguins slide on ice so smoothly?
- What makes a rocket move faster in the sky but slow down in water?
Topic Introduction
Friction is a force that tries to stop things from moving. It acts between two surfaces that are touching like your shoe and the ground, or a tire and the road. Friction resists motion and can both help and hinder us in daily life.
Analogies
- Friction is like invisible glue: It sticks your foot to the ground just enough to stop you from slipping.
- Friction is like a brake: It stops your toy car when you slide it across the floor.
Core Concept Explanation
Causes of Friction
Friction happens because even smooth surfaces have tiny bumps. When two surfaces rub, these bumps get caught on each other, causing friction.
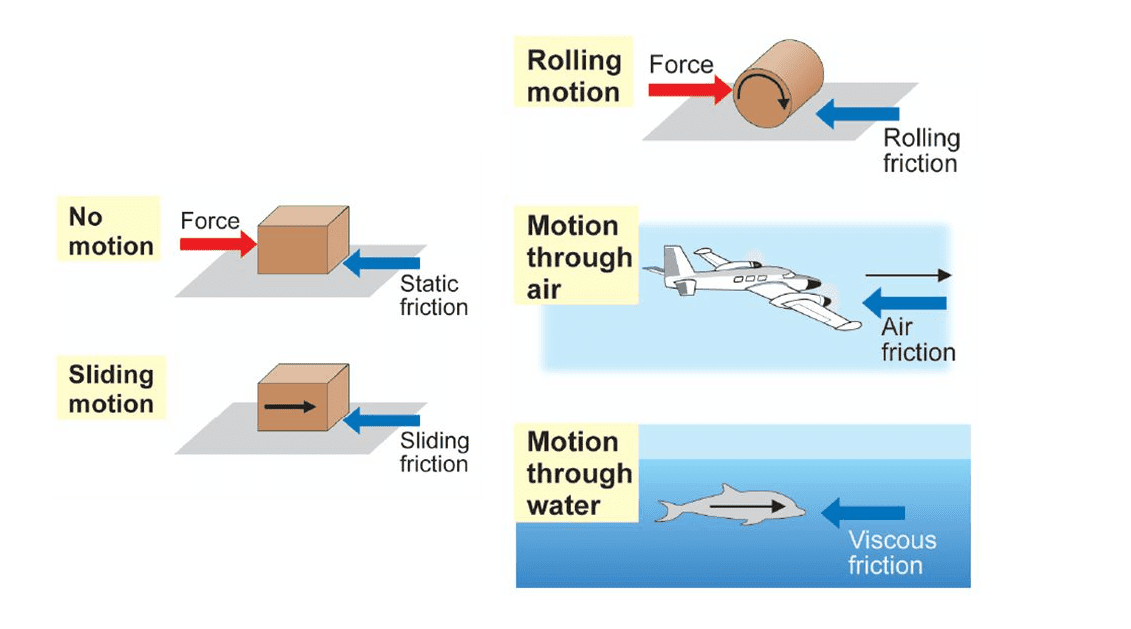
Types of Friction
- Static Friction: Keeps things from moving. Example: A book resting on a table.
- Sliding Friction: Slows down something already moving. Example: Sliding a box on the floor.
- Rolling Friction: Occurs when something rolls. It’s less than sliding friction. Example: A ball rolling.
- Fluid Friction: Happens when an object moves through a fluid (air or water). Example: Swimming in a pool.
Factors Affecting Friction
- Nature of Surfaces: Rough surfaces create more friction; smooth ones, less.
- Weight or Pressure: Heavier objects press down more and create more friction.
- Contact Area: More contact can increase friction, but not always directly.
Advantages of Friction
- Helps us walk without slipping.
- Allows cars to move without skidding.
- Enables writing on paper.
Disadvantages of Friction
- Wears out shoes and machines.
- Produces unwanted heat.
- Wastes energy in moving parts.
Increasing Friction
- Adding roughness (like sand on icy roads).
- Using special materials (like rubber soles for grip).
Reducing Friction
- Using lubricants like oil or grease.
- Polishing surfaces.
- Using ball bearings in machines.
Fluid Friction and Streamlined Shapes
Fluid friction slows down objects in air or water. To reduce it, objects are given streamlined shapes like airplanes, fish, and rockets which cut through fluid more smoothly.
Scale or Context
Friction is present in everything that moves. From writing with a pencil to launching satellites into space, understanding and controlling friction is essential for safety, design, and speed.
DIY Hands-on Activity
Title: Which Surface Slows It Down?
Brief Overview: Explore how different surfaces affect the movement of a toy car.
Materials Needed
- A small toy car
- A ramp (wooden board or book stack)
- Different surface materials: towel, plastic sheet, sandpaper, foil
- Stopwatch
Safety Precautions
- Don’t use very steep ramps.
- Avoid sharp objects like broken plastic or glass.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the ramp at an angle using books.
- Cover the ramp with one surface (e.g., sandpaper).
- Place the toy car at the top and let it go.
- Measure how far and how fast it goes.
- Repeat with different surfaces.
- Record your observations.
Observation/Exploration Task
Which surface slowed the car down the most? Why do you think that happened? What surface helped it go the fastest?
Elaboration Activity
Friction Challenge Discussion: In groups or with family, list as many items as possible in your home or school where friction is helpful vs. where it causes problems. Discuss which could be improved and how.
Explanation & Recap
Friction is a natural force that always acts to resist motion. It can be both useful (like helping us walk) and a challenge (like heating up machines). Engineers often work to manage friction to improve how things move.
Real-Life Applications
Car Design: Engineers design tires with special grooves to increase friction and prevent skidding.
Sports: Athletes wear shoes with grip to increase friction on courts and tracks.
Quick Quiz
1) Which type of friction is the weakest?
a) Static b) Rolling c) Sliding d) Fluid Correct
Answer: b) Rolling
2) What reduces friction in machines?
a) Water b) Grease c) Paper d) Sandpaper
Correct Answer: b) Grease
3) Why do swimmers wear tight suits?
a) To look cool b) To stay dry c) To reduce fluid friction d) To float Correct
Answer: c) To reduce fluid friction
Think-Pair-Share
Imagine you’re designing shoes for astronauts to use on the Moon. What kind of friction should they have? Discuss how you would test the grip on Moon-like surfaces.
Main Recap
- Friction resists motion and is caused by surface roughness.
- There are different types: static, sliding, rolling, and fluid.
- Friction can be both useful and a problem.
- We can increase or decrease it using materials and design.
- Streamlined shapes reduce fluid friction.
Creative Challenge
Design a vehicle that moves through both water and air. What shape would it have to reduce friction in both cases? Draw your design and label the features that help reduce friction.
More to Explore
- Investigate how athletes reduce friction in sports gear.
- Research how bullet trains in Japan use streamlined design.
- Explore how friction works in space does it exist there?
Student Self-Evaluation
☐ I can explain what friction is. ☐ I can describe different types of friction. ☐ I understand where friction helps and where it doesn’t. ☐ I enjoyed doing the activity and learned from it.
Reflection
What was the most surprising thing you learned about friction today? What part of the lesson made you think differently about how things move?
Digital Learning Enhancements
YouTube video Link: Friction – The Force That Opposes Motion
Interactive Simulation Link: Explore how different surfaces and weights affect friction with this PhET Simulation: https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/friction