Unveiling the Invisible: Discovering the World of Atoms and Molecules
Atoms and Molecules Lesson Plan For Class 9
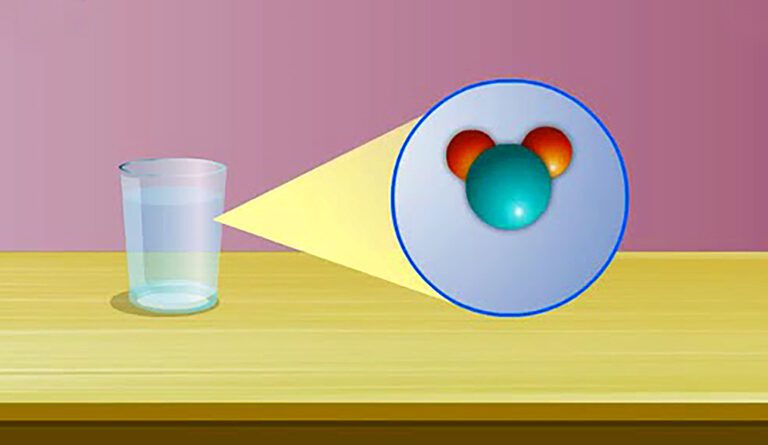
Hook – Whats in a Drop of Water?
Have you ever looked at a drop of water and wondered, “How small can it get?” If you keep dividing it in half again and again, at some point, you reach something so tiny that it cant be divided further in the same way. Thats when you have entered the invisible world of atoms and molecules the building blocks of everything around you.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
-
Understand the basic laws of chemical combination.
-
Define atoms and molecules in simple terms.
-
Learn how to write chemical formulae.
-
Understand the difference between atomic and molecular masses.
-
See how these tiny particles shape everything around us.
Key Vocabulary
-
Atom: The smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction.
-
Molecule: Two or more atoms bonded together.
-
Chemical Formula: A way to represent the types and numbers of atoms in a molecule.
-
Atomic Mass: The mass of a single atom, usually expressed in atomic mass units (u).
-
Molecular Mass: The total mass of all atoms in a molecule.
-
Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
-
Law of Constant Proportions: A given compound always contains the same elements in the same ratio by mass.
Curiosity Questions
-
Why cant we see atoms and molecules with our eyes?
-
Why is water always made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom?
-
How does a small pinch of salt still taste salty whats happening at the atomic level?
Topic Introduction
Everything you see, feel, or touch is made of atoms and molecules. From the air we breathe to the food we eat, all matter is made up of these tiny particles. Scientists discovered that these particles follow certain rules called laws of chemical combination and understanding them helps us make sense of chemical reactions and the materials around us.
Analogies to Understand Complex Ideas
-
Lego Blocks: Atoms are like Lego blocks. You can build anything with them by combining them in different ways just like molecules.
-
Recipe Card: A chemical formula is like a recipe it tells you what and how much to mix to make a substance.
-
Weighing Grocery Items: Atomic and molecular mass are like weights on a scale, helping us measure how much of a substance is involved in a reaction.
Core Concept Explanation
Laws of Chemical Combination
Law 1: Conservation of Mass
In any chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products.
Example: Burning wood does not destroy matter it changes into ash, smoke, and gases.
Law 2: Constant Proportions
A compound always has the same elements in the same ratio.
Example: Water always has hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2:1 (by atoms) or 1:8 (by mass).
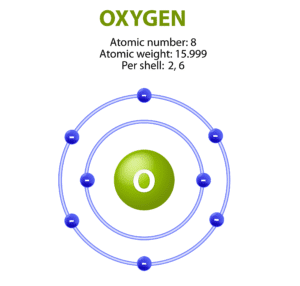
What Are Atoms?
-
Atoms are the basic units of matter.
-
They are incredibly small one strand of hair is millions of atoms thick.
-
Different elements have different types of atoms (e.g., oxygen atom, hydrogen atom).
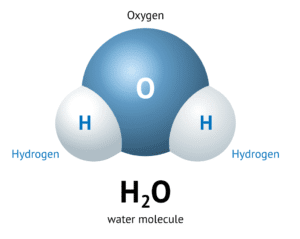
What Are Molecules?
-
Molecules are groups of atoms bonded together.
-
Some molecules have atoms of the same element (e.g., O₂), while others have different atoms (e.g., H₂O).
Chemical Formulae
-
Water: H₂O → 2 Hydrogen atoms + 1 Oxygen atom
-
Carbon dioxide: CO₂ → 1 Carbon atom + 2 Oxygen atoms
-
Subscripts tell you how many atoms of each element are in a molecule.
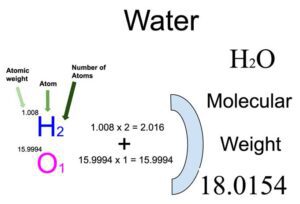
Atomic and Molecular Mass
-
Atomic mass is the mass of one atom of an element.
Example: Hydrogen = 1u, Oxygen = 16u -
Molecular mass is the sum of the atomic masses in a molecule.
Example: H₂O = (2 × 1) + 16 = 18u
Scale or Context
One drop of water contains about 1.67 sextillion molecules thats 1 followed by 21 zeros. Each of those molecules has 3 atoms (2 hydrogen + 1 oxygen). Though invisible, these atoms and molecules make up everything you can see.
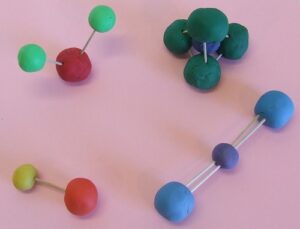
DIY Hands On Activity – Modeling Molecules
Purpose: To understand how atoms combine to form molecules.
Materials:
-
Clay balls or thermocol balls (in 2-3 colours)
-
Toothpicks or matchsticks
-
A marker to label atoms (H, O, C, etc.)
Safety: Avoid sharp objects. Wash hands after use.
Instructions:
-
Use small balls to represent atoms.
-
Join them using toothpicks to form simple molecules:
-
H₂ (2 hydrogen atoms)
-
O₂ (2 oxygen atoms)
-
H₂O (2 hydrogen + 1 oxygen)
-
CO₂ (1 carbon + 2 oxygen)
-
-
Label each atom.
Concept Connection & Deep Explanation
What did we observe?
We built simple molecules using models.
Why did it happen?
Atoms bond in specific ratios to form stable molecules.
What does it show us?
It visually explains the concept of chemical formulae and how different atoms combine to form a compound.
Observation / Exploration
Go around your home and find 5 things that involve molecules (e.g., sugar, water, oxygen, salt, plastic). Research or guess what atoms might be inside each of them.
Elaboration Activity – Atom Theatre
Activity: Act out a role play where students play as different atoms.
-
Some play hydrogen, others oxygen, nitrogen, etc.
-
When a teacher calls “form water”, two hydrogen and one oxygen should form a group holding hands.
-
Reinforces combination rules and ratios in a fun, memorable way.
Real life Applications
-
Medicines: Chemists use molecular formulas to design drugs with the right atoms and ratios.
-
Water Purification: Knowing the molecular mass helps in chemical treatment and reactions.
-
Cooking: Every recipe is like a chemical combination certain elements combining in fixed proportions to form new tastes and textures.
Quick Quiz
-
Which law states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction?
a) Law of Constant Proportions
b) Law of Conservation of Mass
c) Law of Motion -
What is the formula for carbon dioxide?
a) CO
b) CO₂
c) C₂O -
If atomic mass of Oxygen = 16u, what is the molecular mass of O₂?
Think Pair Share
Imagine if atoms did not combine in fixed ratios. What would happen to water, food, or air?
Discuss with a partner: How would life be different without consistent molecules?
Main Recap
-
Atoms are the smallest units of elements.
-
Molecules are groups of atoms bonded together.
-
Laws of chemical combination guide how atoms form compounds.
-
Chemical formulae show what atoms and how many are in a molecule.
-
Atomic and molecular masses help us measure substances accurately.
Creative Challenge
Design a “Molecule Mascot” poster. Pick any everyday molecule like H₂O, CO₂, or CH₄ and turn it into a cartoon character. Label its parts and write a fun fact.
More to Explore
-
Search: “Smallest things in the universe”
-
Watch a 3D model of a water molecule online
-
Try the PhET simulation on building molecules
Student Self-Evaluation
☐ I can explain what atoms and molecules are.
☐ I understood the laws of chemical combination.
☐ I enjoyed building molecule models.
☐ I know how to calculate molecular mass.
Reflection
What was your favourite part of the lesson? Did you like building molecules or acting out atoms? Write 2-3 sentences about how this helped you understand the tiny world around us.
Digital Learning Enhancements
YouTube Animation: Atoms & Molecules
Interactive PhET Simulation: Build a Molecule