How Do Invisible Forces Light Up Our World? – Electricity and Circuits
Electricity and Circuits Lesson Plan For Class 6
Hook
Have you ever flipped a switch and wondered how that tiny click makes a bulb glow or a fan whirl? What if we told you there’s an invisible flow that powers all these wonders?
Learning Objectives
- By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
- Understand what an electric cell is and how it works.
- Identify open and closed electric circuits.
- Differentiate between conductors and insulators.
- Learn how switches control the flow of electricity.
- Know the basic rules of safety while using electricity.
Curiosity Questions
- Can water carry electricity like a wire does?
- Why don’t birds get shocked when sitting on electric wires?
- What’s inside a battery that makes your toy robot move?
Topic Introduction
Electricity is a form of energy that powers our lights, fans, computers, and even your favorite games. To use it safely and smartly, we need to understand how it travels through wires in something called a circuit. Let’s explore this invisible flow.
Analogies
- Think of electricity like water in a pipe. When the pipe is complete, water flows just like electricity in a closed circuit.
- A switch is like a gate on a farm path. If the gate is open, animals can’t cross (no electricity). If it’s closed, they move through easily (electricity flows).
Core Concept Explanation
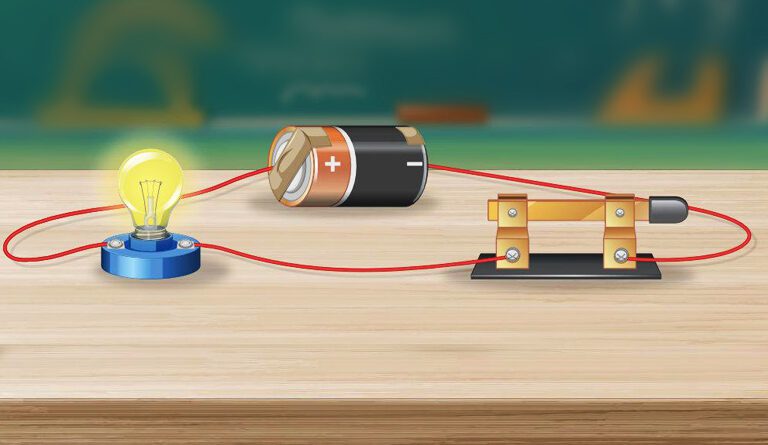
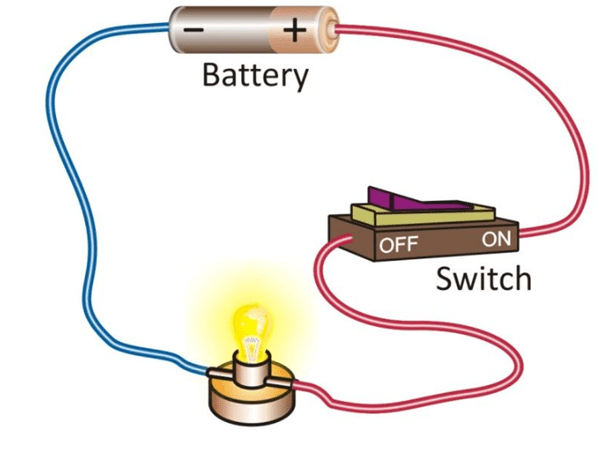
- An electric cell (like a battery) pushes electric current through wires.
- A circuit is a path that electricity follows. When this path is complete (closed circuit), the current flows. When the path is broken (open circuit), the flow stops.
- Conductors allow electricity to pass (like metals), while insulators block it (like plastic).
- A switch opens or closes a circuit and controls the flow of current.
Scale or Context
Electricity can be found in the smallest of devices like earphones to giant cities glowing at night. Whether in a torchlight or a skyscraper, circuits are the heart of the action.
DIY Hands-on Activity
Overview: Build a simple electric circuit to light a bulb.
Materials Needed
- 1 small bulb (torch bulb)
- 1 battery (1.5V or AA)
- 2 wires with clips or foil
- A small plastic switch (or make one with paperclip)
Safety Precautions: Use only low-voltage batteries. Never touch plug points or mains electricity.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Attach one end of the wire to the battery’s positive end.
- Attach the other end to one terminal of the bulb.
- Use a second wire to connect the other bulb terminal to the battery’s negative end.
- Insert a switch in between one of the wires.
- Flip the switch watch the bulb glow.
Observation/Exploration Task
Try removing the switch. Does the bulb stay on? Try replacing wires with plastic strips — what changes?
Elaboration Activity
Form a pretend “Human Circuit” assign students roles (battery, wires, switch, bulb) and pass a ball (representing current) to understand the path electricity takes.
Explanation & Recap
Electric circuits allow electricity to move from a battery to a device (like a bulb). When the path is whole, electricity flows. When it’s broken, it stops. Switches help control this. Materials like metal allow flow; rubber or wood don’t.
Real-life Applications
- All home devices use switches and circuits: fans, TVs, fridges.
- Circuit breakers in homes protect us from electric shocks.
Quick Quiz
- What is a conductor? Name one.
- What happens when you open a switch in a circuit?
- What provides energy in a simple electric circuit?
Think-Pair-Share
If you had to design a toy car powered by a battery, what materials would you use and why?
Main Recap
- Electricity flows through circuits.
- Circuits can be open or closed.
- Switches control the flow.
- Some materials conduct, others insulate.
- Safety is very important when using electricity.
Creative Challenge
Design your own circuit to light two bulbs using one battery. Can you figure out how to make both bulbs glow at the same time?
More to Explore
- Research how electric circuits power a train engine.
- Try making a homemade switch with foil and cardboard.
- Learn about renewable sources of electric power like solar cells.
Student Self-Evaluation
- Can I build a simple circuit on my own?
- Can I explain what a switch does?
- Do I know what makes a material a conductor?
Reflection
What part amazed you the most the glowing bulb, the DIY switch, or finding out how electricity travels?
Digital Learning Enhancements:
YouTube Animation Link: Setting up a Simple Circuit
Interactive Simulation Link: Try this: https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc