Discovering the Secrets of Light: A Journey Through Reflection and Refraction
Light Reflection and Refraction Lesson Plan For Class 10
Hook – Lets Begin With a Wonder
Imagine this: You are standing at the edge of a swimming pool. You drop a coin in the water. As you look down, the coin appears to be at a different spot than where it actually fell. You reach out to grab it, but your hand misses.
Now think about this: Why does a mirror show you reversed from left to right but not upside down?
There is something amazing happening with light here and its not magic. Its science. Ready to explore?
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
-
Explain how light reflects off curved mirrors and forms images.
-
Use the mirror formula and understand image magnification.
-
Understand how light bends (refracts) when it enters a new medium.
-
Use the lens formula and magnification for spherical lenses.
-
Describe what the power of a lens means and how it is used.
Key Vocabulary (with Simple Meanings)
Reflection: When light bounces off a surface, like a mirror.
Refraction: When light bends as it passes from one medium to another (like from air to water).
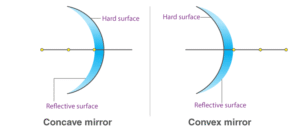
Concave Mirror: A mirror that curves inward like the inside of a spoon.
Convex Mirror: A mirror that curves outward like the back of a spoon.
Focal Length (f): The distance between the mirror/lens and its focus point.
Magnification (M): Tells you how much bigger or smaller an image is compared to the object.
Refractive Index (n): A number that shows how much light bends in a material.
Lens: A transparent object (usually glass or plastic) that bends light to form images.
Power of a Lens (P): Tells how strongly a lens bends light, measured in diopters (D).
Curiosity Questions
-
Why do side mirrors on bikes and cars say “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear”?
-
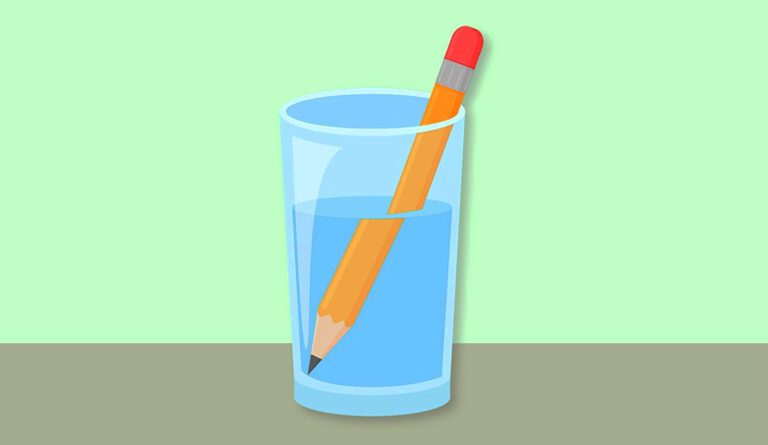
Why does a pencil look bent when dipped in water?
-
Why do people use glasses with convex or concave lenses to see clearly?
Topic Introduction
Light helps us see the world, but its journey is full of interesting twists literally. In this chapter, we will explore how light reflects (bounces back) from mirrors and refracts (bends) through lenses and water.
This topic is not only about school science. Its about how we see, drive, swim, and even take selfies. So, understanding light’s behavior helps us understand everyday life better.
Analogies to Make It Simple
-
Reflection = Ball Bouncing Off a Wall
Just like a ball hits a wall and bounces back, light rays hit a surface and reflect. -
Refraction = Bike Moving from Road to Mud
Imagine a bicycle going from smooth road to muddy ground it slows down and changes direction. Light does the same when moving between different materials. -
Magnifying Glass = Light Focusing Tool
A convex lens is like a magnifying glass. It focuses light at a point, like sunlight burning a piece of paper.
Core Concept Explanation
A. Curved Mirrors
-
Concave Mirrors focus light and form real, inverted images when the object is far away. When the object is very close, the image becomes virtual and enlarged.
-
Convex Mirrors always form virtual, upright, and smaller images.
Mirror Formula:
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
-
f = focal length
-
v = image distance
-
u = object distance (always negative for mirrors)
(All distances are measured from the mirror.)
Magnification (M):
M = -v/u
-
If M is positive → image is virtual and upright
-
If M is negative → image is real and inverted
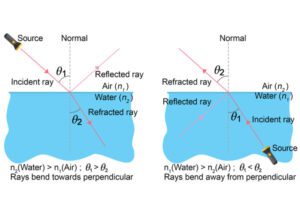
B. Refraction and Refractive Index
Refraction happens because light changes speed when it enters a new medium.
Refractive Index (n):
n = speed of light in vacuum / speed of light in the medium
A higher n means light bends more.
C. Lenses
-
Convex Lenses converge light rays and can form real or virtual images.
-
Concave Lenses diverge light rays and always form virtual, upright, and smaller images.
Lens Formula:
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
(Here, sign convention changes slightly. f is +ve for convex, -ve for concave.)
Magnification:
M = v/u
D. Power of Lens:
P = 100 / f (in cm)
-
Convex lenses have positive power.
-
Concave lenses have negative power.
 Scale and Context
Scale and Context
-
A makeup mirror (concave) makes your face look larger.
-
A shop security mirror (convex) gives a wide view.
-
A spectacle lens is only a few cm wide but corrects your entire field of vision.
-
Giant telescopes use mirrors/lenses over a meter in diameter to see distant galaxies.
DIY Hands On Activity: Bending Light at Home
Purpose: To observe how refraction works.
Materials:
-
A glass of water
-
A pencil or straw
-
A spoon
Safety: No risks, but dont spill water near plugs.
Instructions:
-
Fill a glass halfway with water.
-
Place a pencil in the glass at an angle.
-
Look from the side.
Now try this: Replace the pencil with a spoon. Do you notice any bending or distortion?
Concept Connection: What Did We See?
-
The pencil looks bent or broken at the water surface.
-
This happens because light travels slower in water than air and bends.
-
Thats refraction in action the bending of light as it enters a new medium.
Observation/Exploration
Check out your home mirrors. Are they flat, concave, or convex? Can you guess which ones magnify your face and which make it look smaller? Try looking at your reflection in a spoon both sides.
Elaboration Activity: Light Detective Challenge
Imagine you are a detective who only has mirrors and lenses to investigate a hidden room. Write a story or make a small comic showing how you solve the mystery using reflection and refraction tricks.
Real life Applications
-
Rear View Mirrors: Convex mirrors give a wider view and help avoid accidents.
-
Cameras and Telescopes: Use lenses and mirrors to focus light and capture images.
-
Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses: Use concave or convex lenses to correct vision.
Quick Quiz
-
Which mirror always forms virtual and smaller images?
-
Convex Mirror
-
-
What is the formula for power of a lens?
-
P = 100 / f
-
-
What does a negative magnification mean?
-
The image is real and inverted
-
Think Pair Share
“What if your bathroom mirror was made of a concave mirror instead of a flat one? How would your reflection change?”
Discuss with a partner and share your thoughts with the group.
Main Recap – Key Points
-
Light reflects and follows laws of reflection.
-
Refraction bends light at boundaries between materials.
-
Curved mirrors and lenses form real or virtual images.
-
Mirror and lens formulas help calculate image distances.
-
Power of a lens tells how strongly it bends light.
Creative Challenge
Design a futuristic eyeglass that can zoom in, take photos, and display distance using lenses and mirrors. Draw and label the parts, explaining how light would behave in your design.
More to Explore
Did you know? Some animals like frogs can see underwater and above water at the same time thanks to their lens shape.
Student Self Evaluation
-
I understood how curved mirrors form images: Yes / A bit / Not yet
-
I can explain why a pencil looks bent in water: Yes / A bit / Not yet
-
I liked doing the refraction activity: Yes / Sort of / Not really
Reflection
Think about this lesson. What was the most surprising or fun thing you learned?
Digital Learning Enhancements
YouTube Animation Link: Light Reflection & Refraction
Interactive Simulation: PhET Simulation on Bending Light


 Scale and Context
Scale and Context