Discovering the Secret Life of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Matter and Its States Lesson Plan for Class 5
Hook
What if everything you touched could change its shape? What if water could become rock-hard or float away into the air? Let’s find out what’s really happening in the world around us.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
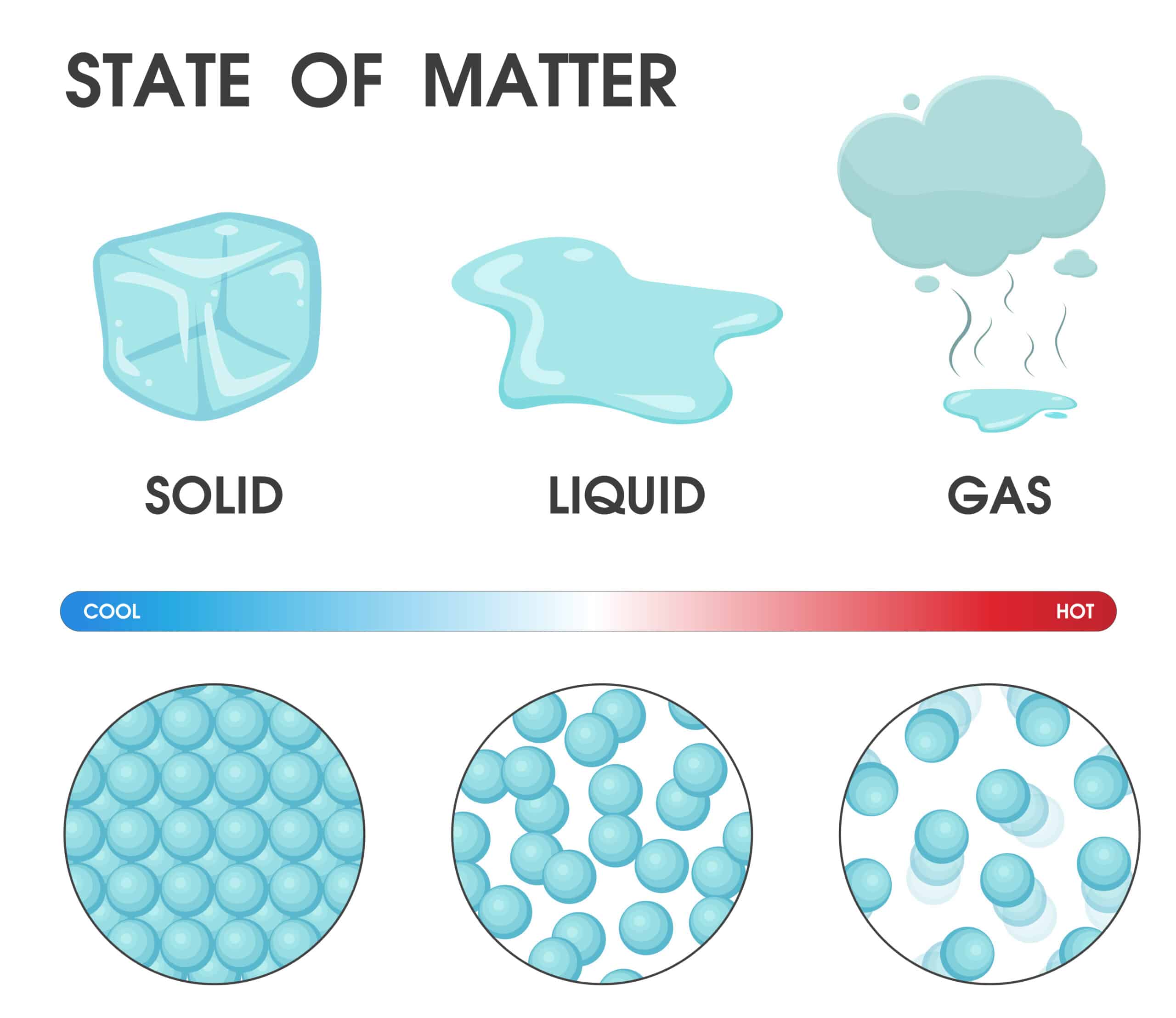
- Identify the three main states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
- Understand how matter changes from one state to another.
- Recognize basic properties of matter such as mass, volume, and density.
Curiosity Questions
- Can air have weight even though we can’t see it?
- Why does ice melt into water but steam rises?
- Why can you stack blocks but not stack juice?
Topic Introduction
Everything around you your books, your water bottle, even the air you breathe is made of matter. Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Matter comes in three main forms called states: solids, liquids, and gases.
Analogies
- Think of solids like Lego blocks they keep their shape and can stack neatly.
- Imagine liquids like a bottle of juice they flow and take the shape of the container.
Core Concept Explanation
Solids have a fixed shape and volume. The particles are tightly packed and vibrate in place. Liquids have a fixed volume but not a fixed shape; their particles move more freely. Gases have no fixed shape or volume. Their particles are far apart and move fast.
Changes in States: When you heat or cool matter, it can change its state. For example:
- Ice (solid) melts into water (liquid)
- Water turns into steam (gas) when heated
- Steam cools down and becomes water again
Properties of Matter:
- Mass is how heavy something is.
- Volume is how much space it takes up.
- Density is how packed the matter is in a space.
Scale or Context
Water turning into steam in a cooker is a small example. But did you know entire clouds are formed when water vapor cools and changes state?
DIY Hands-on Activity
Brief Overview: Let’s explore the states of matter using three simple experiments.
Activity: Melting Ice
Materials Needed
- A few ice cubes
- A transparent cup
- A metal spoon
Safety Precautions
Be careful with sharp ice edges and slippery water.
Instructions:
- Place the ice cube in a cup.
- Observe its shape and hardness (solid).
- Leave it at room temperature for 10 minutes.
- Observe how it melts into liquid water.
- Place it under the sun and see if it evaporates.
Observation Task
Ask students to observe what happens to water in a kettle when heated or in a glass when left outside.
Elaboration Activity
Group Role-play: Assign each student a “particle” role. Ask solid-particles to huddle tightly, liquid-particles to move slowly past each other, and gas-particles to move rapidly around the room.
Explanation & Recap
Matter is everything around us. It exists in three main states. Heating and cooling can change the state. Matter always has mass and takes up space.
Real-life Applications
- Refrigerators turn liquids into solids by freezing
- Airbags in cars use compressed gas to protect passengers
Quick Quiz (3 Questions)
- What are the three main states of matter?
- What happens to water when it’s frozen?
- Which state of matter spreads to fill a container?
Think-Pair-Share
Why do you think hot air balloons rise? Talk with a friend and share your ideas.
Main Recap
- Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass.
- It can be solid, liquid, or gas.
- It changes states when heated or cooled.
Creative Challenge
Design your own “State of Matter Robot” that can change shape and form just like solids, liquids, and gases.
More to Explore
- Research the fourth state of matter: Plasma
- Explore how astronauts manage liquids in space
Student Self-Evaluation
- Can I explain what matter is?
- Can I name the three states?
- Did I enjoy the experiment?
Reflection
What part did you enjoy most the experiment or the group activity? Share your thoughts.
Digital Learning Enhancements
YouTube Animation Link: Changing States of Matter
Interactive Simulation Link: States of Matter

